Scaling Routers with In-Package Optics and High-Bandwidth Memories
By Isaac Keslassy 1,2, Ilay Yavlovich 1, Jose Yallouz 1, Tzu-Chien Hsueh 3, Yeshaiahu Fainman 3, Bill Lin 3
1 Technion
2 UC Berkeley
3 UC San Diego
Abstract
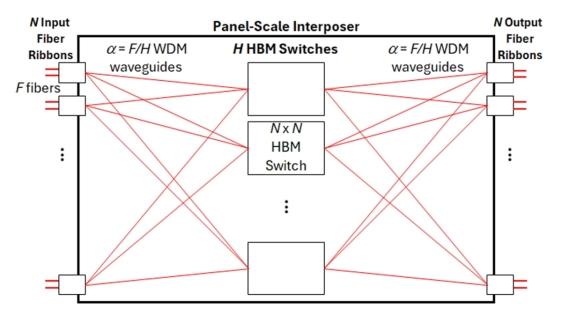
 This paper aims to apply two major scaling transformations from the computing packaging industry to internet routers: the heterogeneous integration of high-bandwidth memories (HBMs) and chiplets, as well as in-package optics. We propose a novel internet router architecture that employs these technologies to achieve a petabit/sec router within a single integrated package. At the top-level, we introduce a novel split-parallel switch architecture that spatially divides (without processing) the incoming fibers and distributes them across smaller independent switches without intermediate OEO conversions or fine-tuned per-packet load-balancing. This passive spatial division enables scaling at the cost of a coarser traffic load balancing. Yet, through extensive evaluations of backbone network traffic, we demonstrate that differences with fine-tuned approaches are small. In addition, we propose a novel HBM-based shared-memory architecture for the implementation of the smaller independent switches, and we introduce a novel parallel frame interleaving algorithm that packs traffic into frames so that HBM banks are accessed at peak HBM data rates in a cyclical interleaving manner. We further discuss why these new technologies represent a paradigm shift in the design of future internet routers. Finally, we emphasize that power consumption may constitute the primary bottleneck to scaling.
This paper aims to apply two major scaling transformations from the computing packaging industry to internet routers: the heterogeneous integration of high-bandwidth memories (HBMs) and chiplets, as well as in-package optics. We propose a novel internet router architecture that employs these technologies to achieve a petabit/sec router within a single integrated package. At the top-level, we introduce a novel split-parallel switch architecture that spatially divides (without processing) the incoming fibers and distributes them across smaller independent switches without intermediate OEO conversions or fine-tuned per-packet load-balancing. This passive spatial division enables scaling at the cost of a coarser traffic load balancing. Yet, through extensive evaluations of backbone network traffic, we demonstrate that differences with fine-tuned approaches are small. In addition, we propose a novel HBM-based shared-memory architecture for the implementation of the smaller independent switches, and we introduce a novel parallel frame interleaving algorithm that packs traffic into frames so that HBM banks are accessed at peak HBM data rates in a cyclical interleaving manner. We further discuss why these new technologies represent a paradigm shift in the design of future internet routers. Finally, we emphasize that power consumption may constitute the primary bottleneck to scaling.
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- DPIQ Tx PICs
- IMDD Tx PICs
- Near-Packaged Optics (NPO) Chiplet Solution
- High Performance Droplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
Related Technical Papers
- Intel Delivers Cutting-Edge Process Technologies to the Data Center with Intel 18A and Advanced Chiplet Packaging
- Understanding In-Package Optical I/O Versus Co-Packaged Optics
- Understanding In-Package Optical I/O Versus Co-Packaged Optics
- Occamy: A 432-Core 28.1 DP-GFLOP/s/W 83% FPU Utilization Dual-Chiplet, Dual-HBM2E RISC-V-based Accelerator for Stencil and Sparse Linear Algebra Computations with 8-to-64-bit Floating-Point Support in 12nm FinFET
Latest Technical Papers
- Scaling Routers with In-Package Optics and High-Bandwidth Memories
- TDPNavigator-Placer: Thermal- and Wirelength-Aware Chiplet Placement in 2.5D Systems Through Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
- Towards Scalable Multi-Chip Wireless Networks with Near-Field Time Reversal
- Hybrid surface pre-treatments for enhancing copper-to-copper direct bonding
- Toward Digital Twins in 3D IC Packaging: A Critical Review of Physics, Data, and Hybrid Architectures