LaMoSys3.5D: Enabling 3.5D-IC-Based Large Language Model Inference Serving Systems via Hardware/Software Co-Design
By Qipan Wang 1, Zhe Zhang 3, Shuangchen Li 3, Hongzhong Zheng 3, Zheng Liang 2, Yibo Lin 1, Runsheng Wang 1, Ru Huang 1
1 Peking University, China
2 University of California, Berkeley, USA
3 Alibaba DAMO Academy and Hupan Lab, China
Abstract
 The success of large language models (LLMs) amplifies the need for high-throughput, energy-efficient inference at scale. 3D-DRAM–based accelerators provide high memory bandwidth and therefore an opportunity to accelerate the bandwidth-bound decode phase. However, how to adequately balance compute density for prefill with bandwidth/capacity for decode remains open. Moreover, most prior designs do not target end-to-end serving, leaving the co-design of dataflow, parallel mapping, and scheduling underexplored.
The success of large language models (LLMs) amplifies the need for high-throughput, energy-efficient inference at scale. 3D-DRAM–based accelerators provide high memory bandwidth and therefore an opportunity to accelerate the bandwidth-bound decode phase. However, how to adequately balance compute density for prefill with bandwidth/capacity for decode remains open. Moreover, most prior designs do not target end-to-end serving, leaving the co-design of dataflow, parallel mapping, and scheduling underexplored.
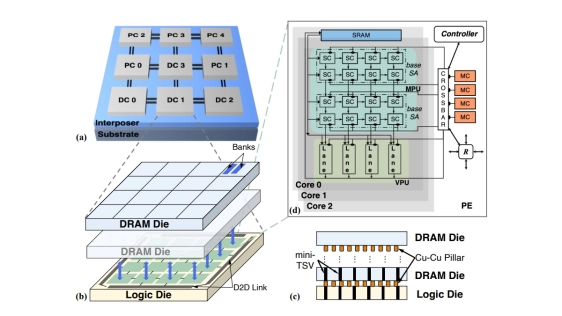
To bridge the gap, we present LaMoSys3.5D, to our knowledge the first scalable 3.5D-IC architecture for LLM serving. LaMoSys3.5D composes heterogeneous 3D-DRAM chiplets on a 2.5D interposer: compute-rich chiplets for prefill and bandwidth- /capacity-rich chiplets for decode. To realize efficient serving, we adopt a hardware–software co-design spanning dataflow, parallel mapping, and introduce a thermal-aware modeling and hierarchical design-space exploration framework. Across diverse LLMs and workloads, LaMoSys3.5D improves throughput-per-watt over DGX-A100 systems by 62% and achieves a 4.87× better endto-end latency (geo-mean) versus prior 3D designs. We further distill intriguing design guidelines for 3.5D-IC architectures and end-to-end inference serving.
Index Terms—Large Language Model, Inference Serving, 3.5DIC, Chiplet Integration, Hardware/Software Co-Design
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
- 12nm EURYTION RFK1 - UCIe SP based Ka-Ku Band Chiplet Transceiver
- Bridglets
- Automotive AI Accelerator
- Direct Chiplet Interface
Related Technical Papers
- Chiplet Cloud: Building AI Supercomputers for Serving Large Generative Language Models
- Chiplet Cloud: Building AI Supercomputers for Serving Large Generative Language Models
- Hecaton: Training and Finetuning Large Language Models with Scalable Chiplet Systems
- A3D-MoE: Acceleration of Large Language Models with Mixture of Experts via 3D Heterogeneous Integration
Latest Technical Papers
- LaMoSys3.5D: Enabling 3.5D-IC-Based Large Language Model Inference Serving Systems via Hardware/Software Co-Design
- 3D-ICE 4.0: Accurate and efficient thermal modeling for 2.5D/3D heterogeneous chiplet systems
- Compass: Mapping Space Exploration for Multi-Chiplet Accelerators Targeting LLM Inference Serving Workloads
- Chiplet technology for large-scale trapped-ion quantum processors
- REX: A Remote Execution Model for Continuos Scalability in Multi-Chiplet-Module GPUs